
Cleanrooms are very costly to build and maintain because they have to be customized in accordance with the product. They are designed to establish minimum contamination. Thus, validation of cleanroom is very essential.
While building or extending the cleanroom, it is important to design it right from the outset to ensure that all requirements are met in the initial stage because, changes done afterwards could be very costly.
Cleanroom Design Considerations
The environment in the pharmaceutical industry and in the manufacture of medical devices is highly regulated and needs continuous assurance that critical processes are performed within controlled conditions that have been validated, in order to produce the desired outcomes.
Following points are necessary to demonstrate validation of a cleanroom environment:

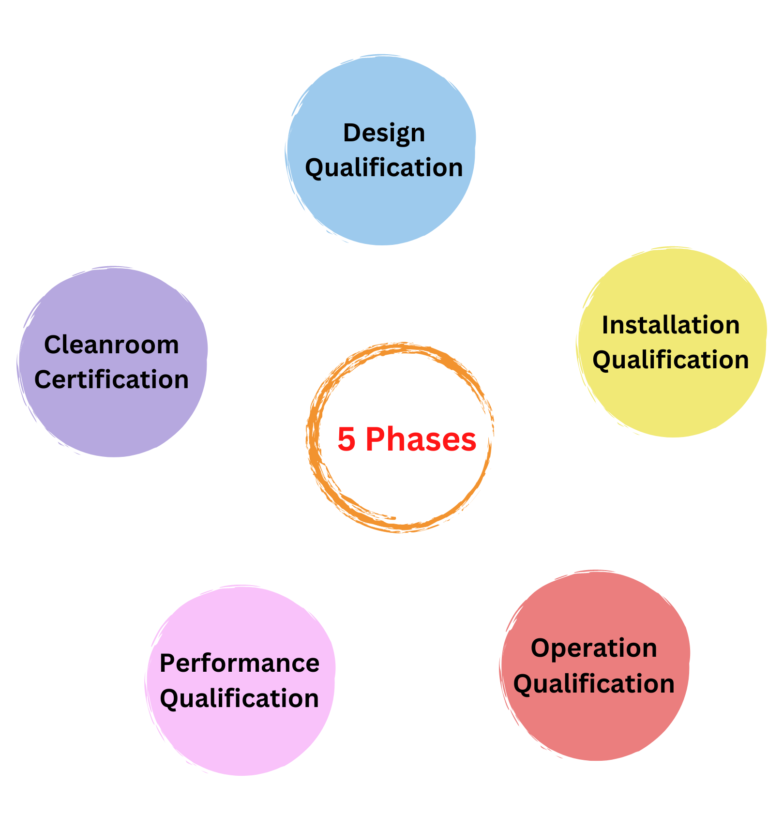
Cleanroom Validation Life Cycle
Cleanroom is certified to a specific class according to the ISO 14544-1 indicating its level of control. The process of designing, building, and validation testing and certification of a cleanroom involves 5 phases. Each phase is consistent with implementing, designing, and testing to specific requirements.
- Phase 1: Phase 1 is referred as ‘Design Qualification’. The purpose of this phase is to provide objective evidence that the design is fit for its intended purpose. It is documented verification against the requirements defined in the acceptance criteria of respective DQ protocol. The approval of the design qualification is a pre-requisite requirement for the initiation of the installation qualification.
- Phase 2: Phase 1 is also referred as ‘Installation Qualification’ or ‘As Built’ testing. Testing is performed with all services connected and working, but materials, production equipment, or employees are absent. This testing proves that the equipment is correctly installed.
- Phase 3: Phase 2 is the ‘Operational Qualification’ or ‘At Rest’ testing. Testing is done when the equipment is installed but not operating, and employees are not present. This testing confirms that the equipment works properly to achieve the required environmental conditions.
- Phase 4: Phase 3 is referred as ‘Performance Qualification’. This phase involves testing which is performed with all equipment installed and operating and employees performing their regular work duties and tasks. This testing confirms that the cleanroom has the required operational performance for the cleanroom application.
- Phase 5: ‘Cleanroom Certification’ is the last stage. Validation of cleanrooms is done for a required cleanliness class. The chosen level of cleanliness is determined according to the needs of the users. Cleanroom classes are described in ISO1464-1 and methods for evaluation and measurement for certification are specified in ISO14644-3.
For Cleanroom Validation Certification, ISO 14644-3 lists some tests, a few of which are listed below:
- Airborne particle count test
- Airflow test
- Air pressure differential test
- Filter leakage test
- Flow visualization test
- Airflow direction test
- Temperature test
- Humidity test
- Recovery test
- Containment leak test
Once certified, the cleanroom factors need to be monitored to make sure that the parameters have not changed or drifted, and that the environment is under control. A constant monitoring program is required after certification as well. Cleanroom validation is much more than simply counting the particles. It involves various tests that must be performed in different cleanroom states to verify that the cleanroom is fit for its intended use along with meeting all the stipulations set forth for the requirements of classification governing the cleanroom application.
It is essential to note that different cleanrooms will use the different procedures. So, you needs to follow your specific cleanroom or company procedure depending on the product for which cleanroom validation is being done.
